Centrifugal Pump
Everything Explained about Centrifugal Pumps | Types, working and features of Centrifugal Pumps
What is Centrifugal Pump?
Centrifugal pumps are used to transport fluids by the conversion of rotational kinetic energy to the hydrodynamic energy of the fluid flow. The rotational energy typically comes from an engine or electric motor. They are a sub-class of dynamic axisymmetric work-absorbing turbomachinery. The fluid enters the pump impeller along or near the rotating axis and is accelerated by the impeller, flowing radially outward into a diffuser or volute chamber (casing), from which it exists.
What are the uses of Centrifugal Pumps?
Common uses include water, sewage, agriculture, petroleum, and petrochemical pumping. Centrifugal pumps are often chosen for their high flow rate capabilities, abrasive solution compatibility, mixing potential, as well as their relatively simple engineering. A centrifugal fan is commonly used to implement an air handling unit or vacuum cleaner. The reverse function of the centrifugal pump is a water turbine converting the potential energy of water pressure into mechanical rotational energy.
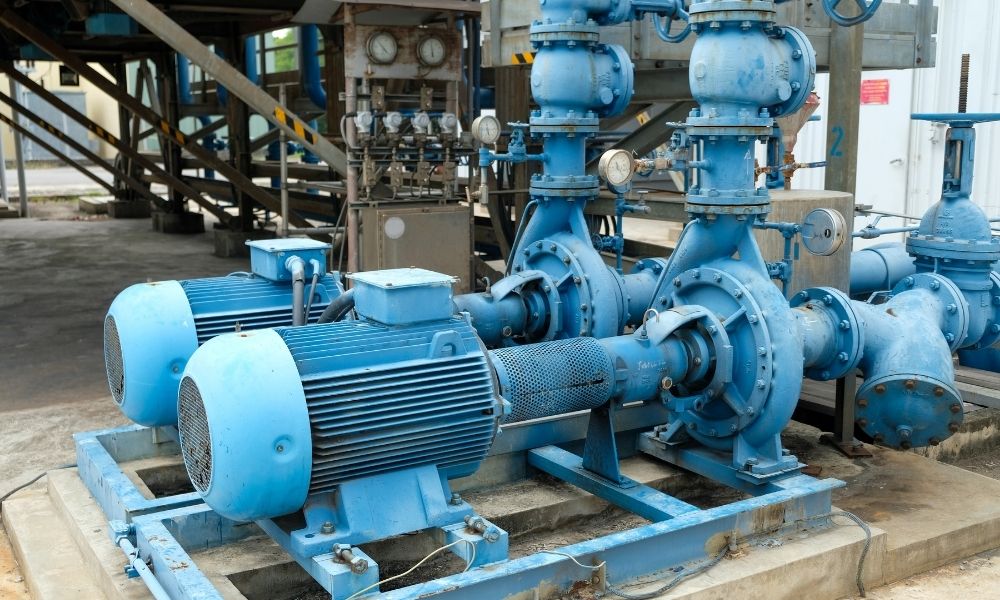

How Centrifugal Pump Works?
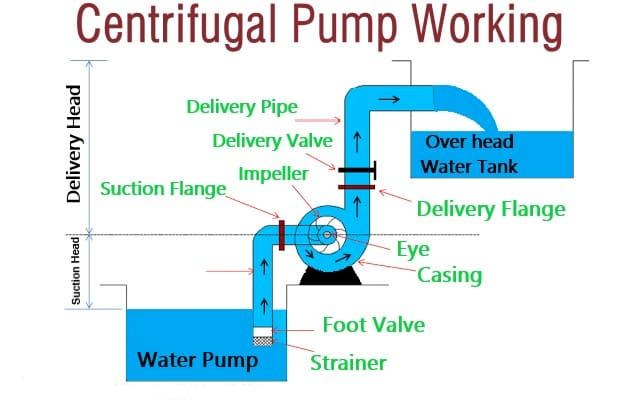
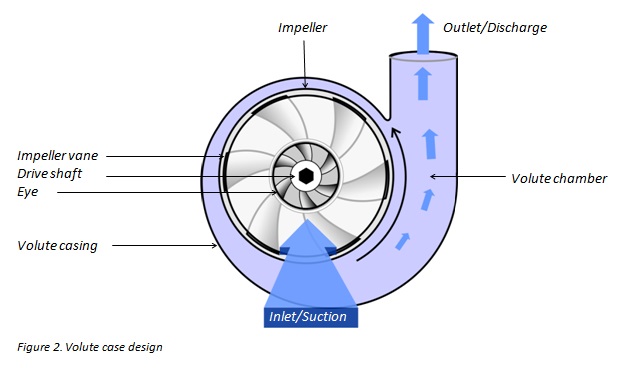
Like most pumps, a centrifugal pump converts rotational energy often from a motor to energy in a moving fluid. A portion of the energy goes into the kinetic energy of the fluid. Fluid enters axially through the eye of the casing, is caught up in the impeller blades, and is whirled tangentially and radially outward until it leaves through all circumferential parts of the impeller into the diffuser part of the casing. The fluid gains both velocity and pressure while passing through the impeller. The doughnut-shaped diffuser, or scroll, a section of the casing decelerates the flow and further increases the pressure.
What are the main features of a centrifugal pump?
There are two main families of pumps: centrifugal and positive displacement pumps. In comparison to the latter, centrifugal pumps are usually specified for higher flows and for pumping lower viscosity liquids, down to 0.1 cP. In some chemical plants, 90% of the pumps in use will be centrifugal pumps. However, there are a number of applications for which positive displacement pumps are preferred.
For Further Information and query get in touch with our support team.
This form is currently undergoing maintenance. Please try again later.
Following are the main parts of centrifugal pumps, Impeller. The impeller is a rotor used to increase the kinetic energy of the flow. Casing (Volute). The casing contains the liquid and acts as a pressure containment vessel that directs the flow of liquid in and out of the centrifugal pump. Shaft (Rotor). The impeller is mounted on a shaft. A shaft is a mechanical component for transmitting torque from the motor to the impeller. Shaft sealing. Centrifugal pumps are provided with packing rings or mechanical seal which helps prevent the leakage of the pumped liquid. Bearings. Bearings constrain the relative motion of the shaft (rotor) and reduce friction between the rotating shaft and the stator. What are the main parts of centrifugal pump?
